Technical Information
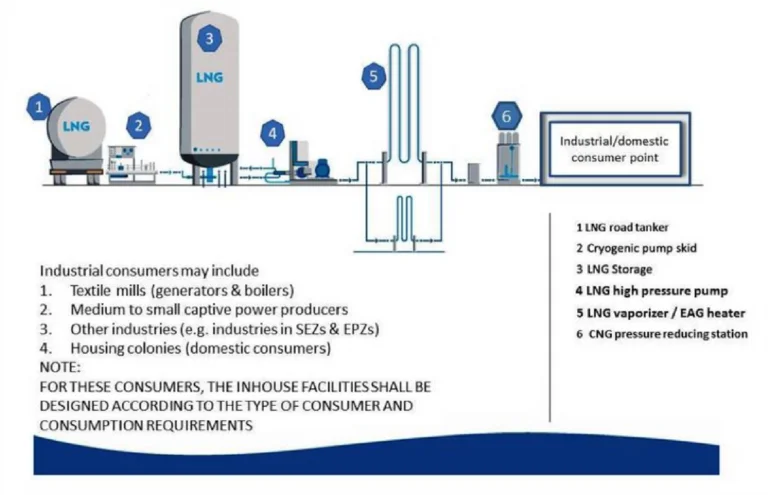
LNG & CNG DISPENSING UNITS & INDUSTRIAL / HOUSING CONSUMERS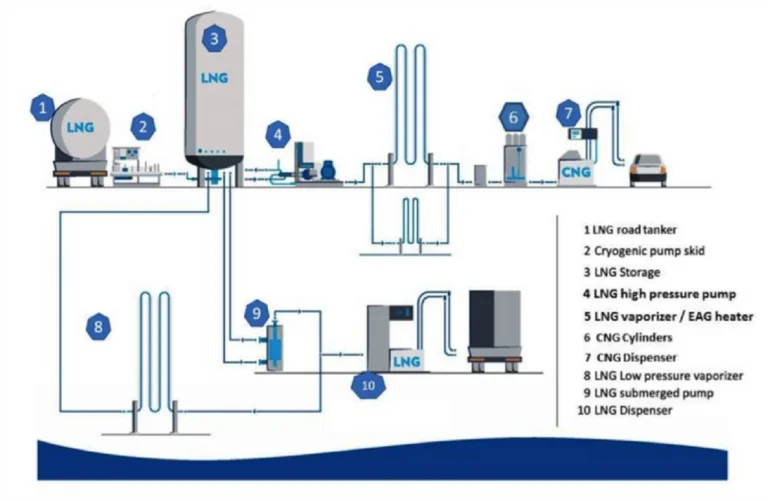
Equipment Specifications
Following Equipment Specifications are based on initial estimates and shall be confirmed during
detailed design per each installation as per requirement.
Marine (Un) Loading Arm & Boil-Off Gas Return Arm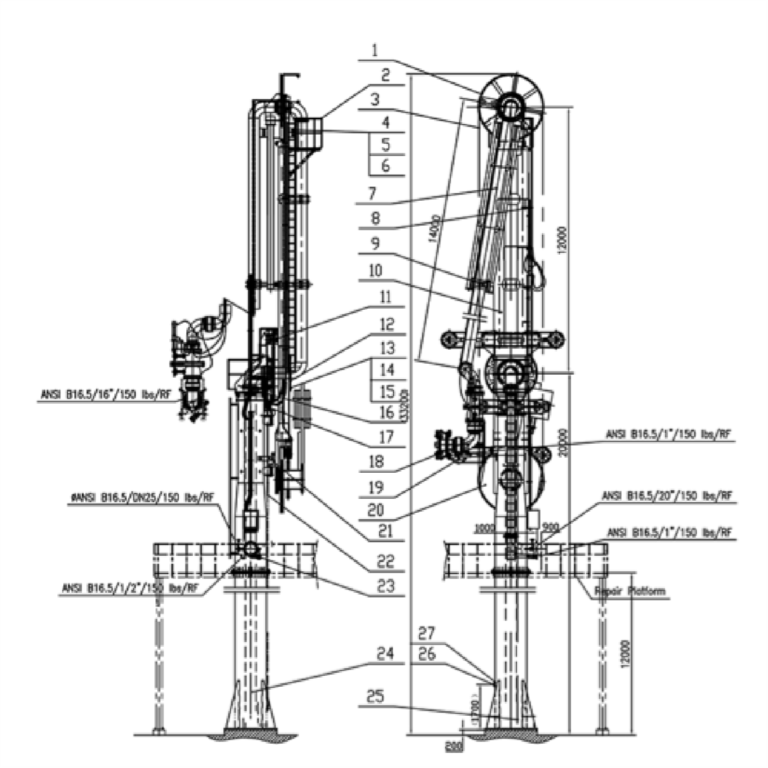
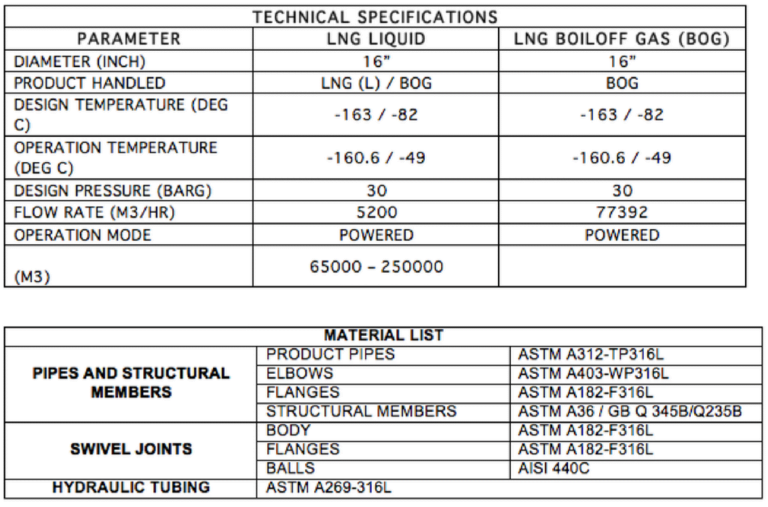
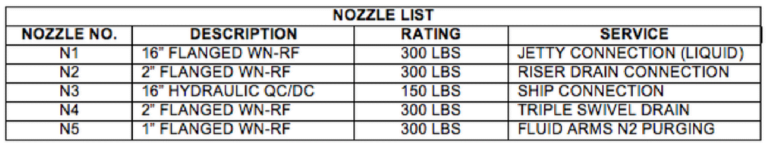
NOTES:
- The dimensions will be finalized, when the cargo ship
manifold, draft operating envelope is known. - Interconnecting piping, valves & fittings, safety systems,
instrumentation and controls, shall be done at detailed
design.
Metering-Skid for NLG Receiving from Ship & Loading of Cryogenic ISO Tankers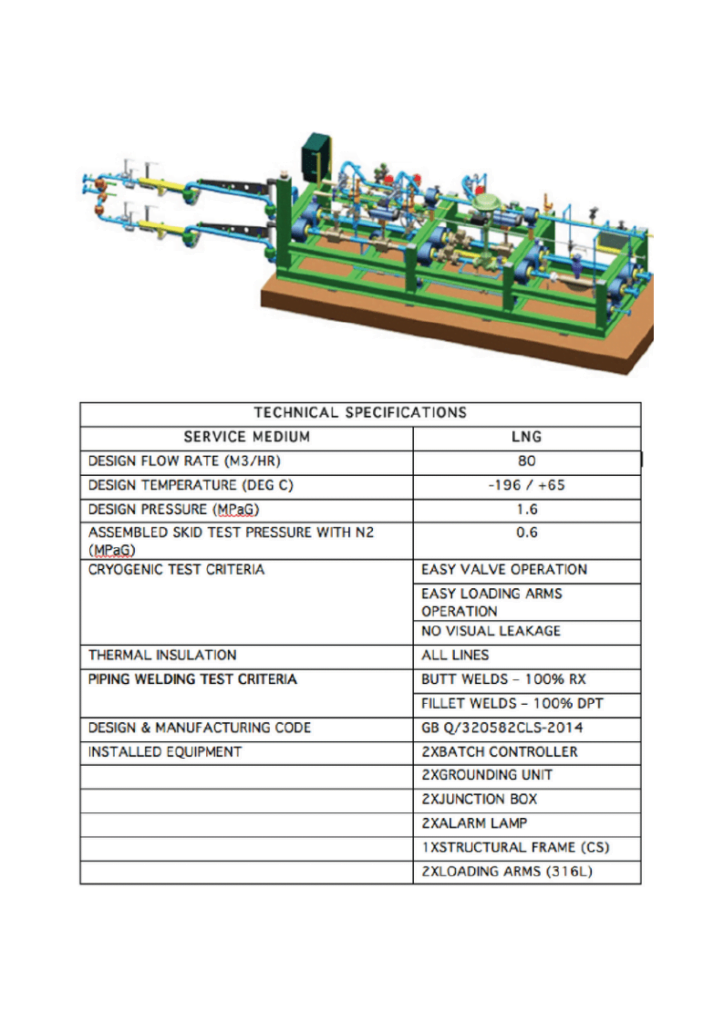
Notes:
Following to be part of detailed design:
- Interconnecting piping, valves & fittings
- Safety systems
- Instrumentations & controls
LNG & CNG DISPENSING UNITS & INDUSTRIAL / HOUSING CONSUMERS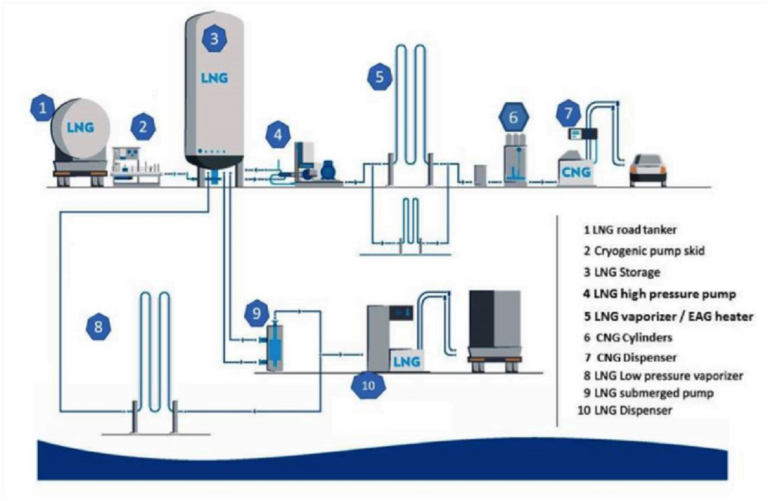
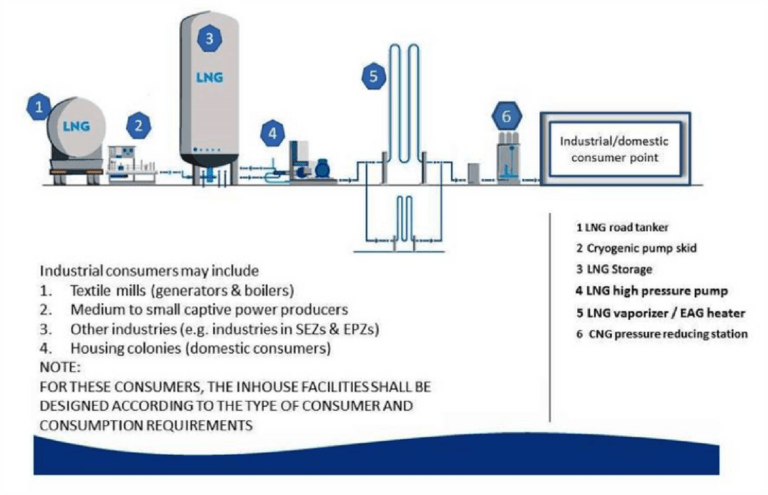
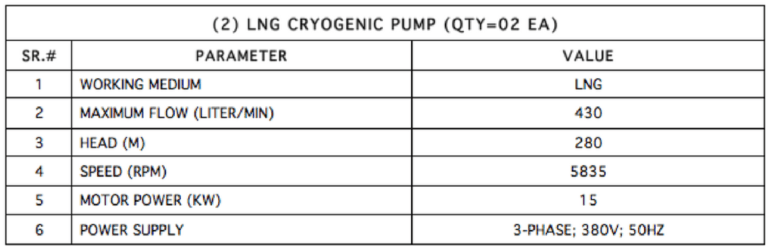
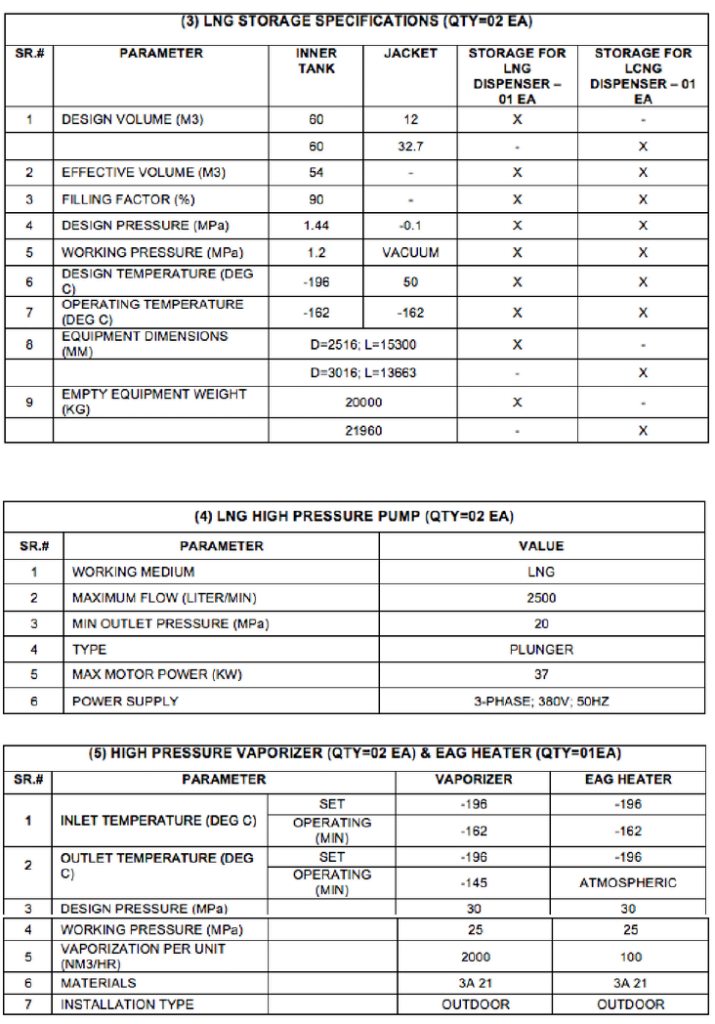
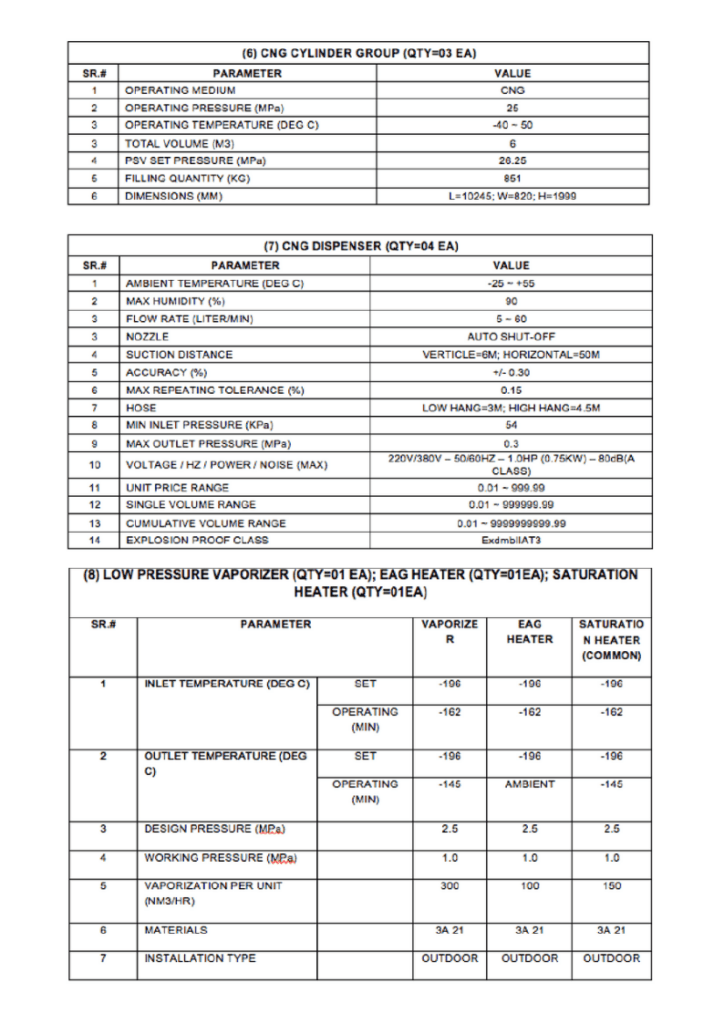
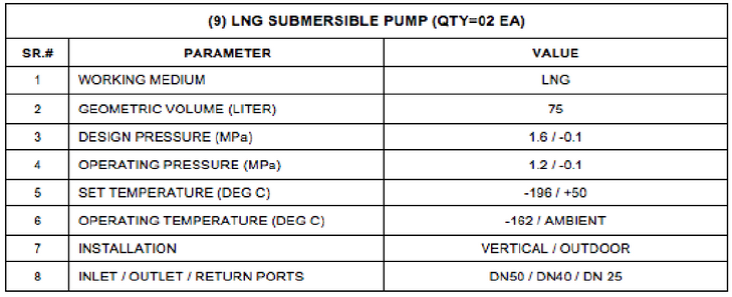
Notes:
Following to be part of detailed design:
- Interconnecting piping, valves & fittings
- Safety systems
- Instrumentations & controls
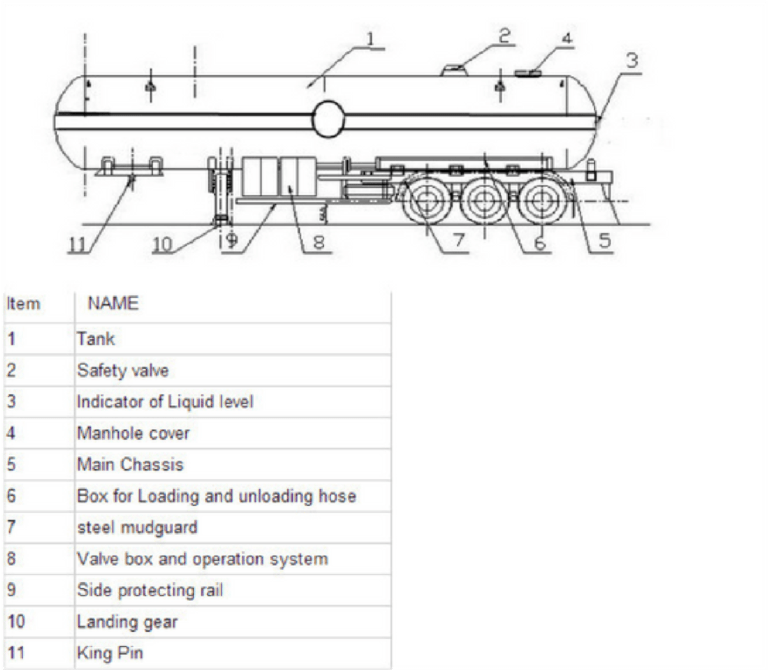
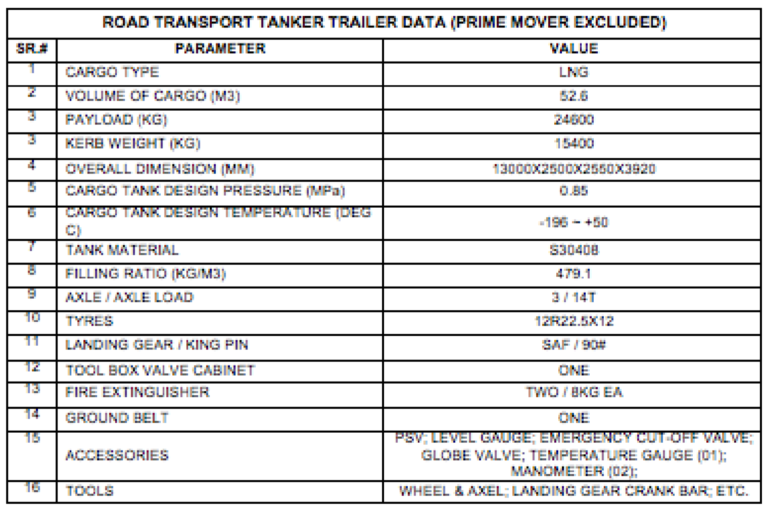
LNG TRANSPORT VEHICLE

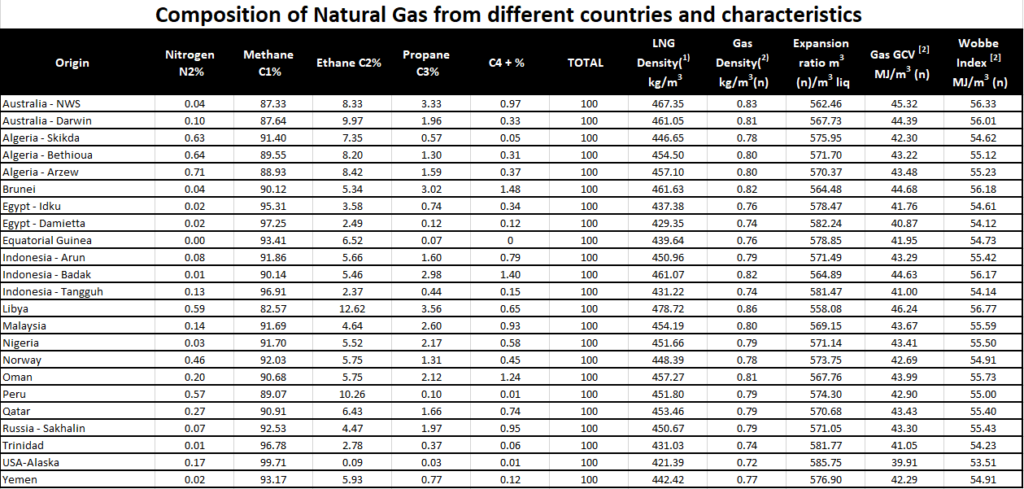
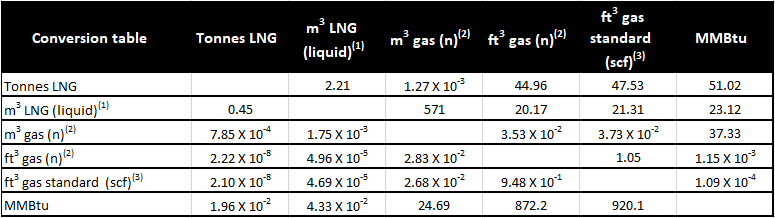
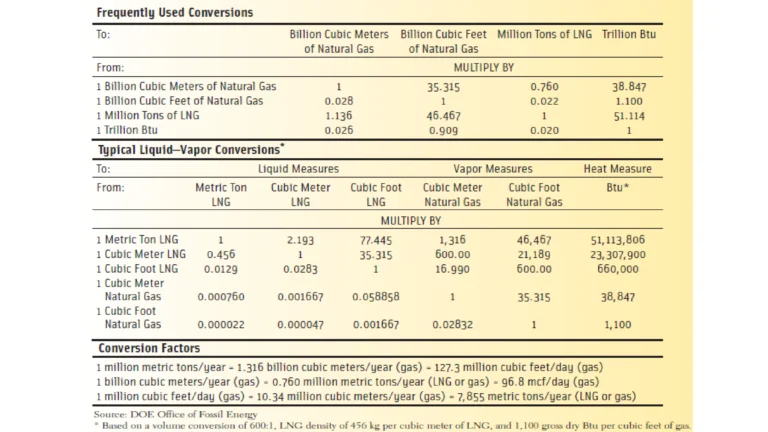
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
FSU Specifications:
The FSU specifications are currently under evaluation. However, the general specifications are given below:
| Sr. No | Description | Unit | Capacity/Dimension |
| 1 | Length Overall | Meters | 288.18 |
| 2 | Breath moulded | Meters | 44.2 |
| 3 | Draught moulded | Meters | 11.35 |
| 4 | LNG capacity | Cum | 150,000 |
| Sr. No | Description | Unit | Capacity/Dimension |
| 1 | Length Overall | Meters | 294.07 |
| 2 | Breath moulded | Meters | 46 |
| 3 | Draught moulded | Meters | 11.6 |
| 4 | LNG capacity | Cum | 170,000 |
LNG and Safety
LNG is natural gas that is converted to liquid by cooling it to minus 162 C. This reduces its volume by a factor of 600 and allows for its safe and efficient storage and transport. LNG is not pressurized, is odorless, non-toxic and non-corrosive. Natural gas is lighter than air, which makes it harder to accumulate in case of any leak. Natural gas has a higher explosion limits (5% – 15%) in air than LPG does (2.11% – 9.6%).
LNG Storage
Storage tanks are specifically built for cryogenic temperature fluids. The tanks keep the liquid at low temperatures to minimize evaporation. LNG storage tanks consist of two concentric shells. Vacuum is applied between the shells to reduce convective heat transfer. The inner shell is made of alloy steel and the outer shell is of carbon steel.
LNG Spills Detection
Electronic methane gas detectors are used for gas detection.
Additionally, due to the cryogenic nature of LNG vapors, air moisture will condense into a visible cloud in the presence of an LNG spill.
LNG does not pollute natural resources such as ground water, soil, wetlands, streams and beaches. It vaporizes quickly and completely.
Is LNG Flammable
LNG is not flammable in its liquid state, but it is flammable as a vapor mixed with air. Due to the rapid evaporation of LNG when exposed to ambient temperatures, natural gas vapors are present immediately upon exposure to the environment. In order for combustion to occur, the percentage of natural gas present in the air must be between five and fifteen percent.
The ignition of an unconfined LNG vapor cloud by typical ignition sources does not produce a pressure wave. However, ignition of LNG vapors in a confined space can produce overpressures strong enough to cause severe damage.
Health Effects
Workers can receive cryogenic burns from direct body contact with cryogenic liquids, metals and cold gases. LNG vapors are considered to be non-toxic by inhalation.
Health, Safety, Environment Policy
Comprehensive policy covering all aspects of LNG handling and operations to be in place.
Training and awareness sessions for all personnel.
Regular safety drills and awareness sessions.
Hazardous Materials management
1. LNG storage tanks and components as per internationally recognized standards for structural design integrity and operational performance to avoid failures and to prevent fires and explosions.
2. Provisions for over fill protection, secondary containment, metering and flow control, fire protection and grounding to prevent electrostatic charge.
3. Periodic inspections for corrosion and structural integrity along with regular maintenance and replacement of equipment.
4. Loading and unloading activities to be conducted by properly trained personnel according to pre-established formal procedures
5. Flaring is an important safety measure used at LNG facilities to ensure that gas is safely disposed-off in the event of an emergency or power or equipment failure.
6. After LNG liquefication, stored LNG emits a small amount of methane gas vapor known as boil-off gas (BOG), due to heat gain from ambient conditions and tank pumps, in addition to barometric pressure changes. BOG is collected using an appropriate vapor recovery system and could be used as fuel.
7. Guidelines and training for lifting and placing of containers.
8. Operation instruction on loading the containers on flatbeds.
9. Work Instructions and trainings for dispensing LNG.